Long story short: Time to get the basics and tips covered related to the bike or motorcycle engine oil and types right here in this article.
Engine oil is crucial for a motorcycle to run, just as blood is for people. Without oil, the engine will not work. It plays several key roles that help the engine last longer. In India, bike owners should learn about the different types, grades, and how often to change engine oil.
Many of us depend on technicians for oil changes, but it helps to know the basics ourselves. Understanding bike engine oil can make a big difference. This article shares simple tips and advice.
Key Takeaways
- There are mainly three types of bike engine oil, and they are Mineral Oils (MO), Semi-Synthetic Oils and Fully Synthetic Oil (FS).
- Fully synthetic engine oil costs the most, but it’s made from pure chemicals instead of crude oil. It’s best for high-performance bikes, such as off-road or racing models. This oil lasts longer and gives excellent protection.
- The name SAE number also refers to the engine oil grade code. SAE refers to the Society of Automotive Engineers. The letter W refers to ‘Winter’ in the code.
- The first number refers to how oil flows when cold, such as during engine start-up. The second number is defined by how oil flows at higher temperatures than those of a standard engine operating temperature.
- Thin, low-viscosity oils flow more easily to protect engine parts at cold temperatures. Thick, high-viscosity oils are typically more effective at maintaining film strength, which protects engines at high temperatures.
How motorcycle engine oil works
Motorcycle engine oil performs several key tasks to protect and enhance engine performance, including lubrication, cooling, cleaning, and cushioning engine components.
- Lubrication: Engine oil puts a thin layer between moving metal parts, like the pistons and the crankshaft, so they don’t rub directly against each other. This helps reduce wear and tear.
- Cooling: When the engine runs fast, it gets hot. Oil helps by removing heat from critical parts, allowing the engine to run smoothly without overheating.
- Cleaning: As oil moves around inside the engine, it picks up tiny pieces of dirt and metal. It carries these things to the oil filter, which catches them, preventing them from damaging the engine.
- Sealing: Oil helps close small gaps between the piston rings and the walls inside the cylinder. This maintains engine power and prevents gases from leaking, allowing the engine to function more efficiently.
- Protection under pressure: Through oil pumps, the oil is circulated under pressure to reach hard-to-access areas such as bearings and cam lobes, ensuring all critical points receive lubrication even at high RPMs.
Most motorcycles use a wet sump system, where oil sits in a pan at the bottom of the engine. An oil pump sends the oil through the engine to keep parts moving smoothly. In some two-stroke bikes, oil mixes with fuel to lubricate the engine as the fuel-air mix passes through.
After circulating, the oil flows back down to the sump and cools before starting the cycle again. This ongoing process helps the engine run smoothly, even when you ride in tough conditions.
Types of motorcycle engine oil
There are mainly three types of bike engine oil, and they are
- Mineral Oils (MO)
- Semi-Synthetic Oils (SS)
- Fully Synthetic Oil (FS)
Let’s take a closer look at each type of bike engine oil.
1. Mineral Oil (MO)
Mineral oils come from processed petroleum and are the cheapest choice for small engines. These engines don’t usually run fast or face heavy loads. New or smaller bikes often use mineral oil, but it needs to be changed more often and doesn’t last as long.
Pros of mineral oil
- Low cost compared to synthetic oils.
- Ideal for commuter bikes and older motorcycles.
- Provides adequate protection and lubrication for engines running at low mechanical outputs.
Cons of mineral oil
- Lower resistance to oxidation and heat leads to increased fuel consumption and reduced engine performance.
- Needs to be changed more frequently than synthetic oils.
- It is not suitable for high-performance bikes or in extreme conditions.
2. Semi-Synthetic Oil (SS)
Semi-synthetic oil mixes the protection of mineral oil with the better performance of synthetics. It’s a good choice for bikes with 150-300cc engines and costs more than mineral oil. For bikes under 150cc, mineral oil is usually the better option.
Pros of semi-synthetic oil
- Provides better oxidation resistance and improved low-temperature properties compared to mineral oil.
- Offers added protection against oxidation and is suitable for various motorcycle engines.
- More economical than fully synthetic oils while still offering good protection.
Cons of semi-synthetic oil
- It may not offer the same level of performance and protection as fully synthetic oils.
- The level of synthetic oil in the blend can vary, affecting performance.
3. Fully Synthetic Oil
Fully synthetic engine oil costs the most, but it’s made from pure chemicals instead of crude oil. It’s best for high-performance bikes, such as off-road or racing models. This oil lasts longer and gives excellent protection.
Pros of Fully Synthetic Oil
- Excellent heat resistance properties and a high level of lubrication.
- Provides superior performance, low viscosity, and high tolerance to temperature extremes.
- Reduces engine drag, prevents sludge buildup, and extends the time between oil changes.
Cons of Fully Synthetic Oil
- More expensive than mineral and semi-synthetic oils.
- Overkill for motorcycles that do not require high-performance oil.
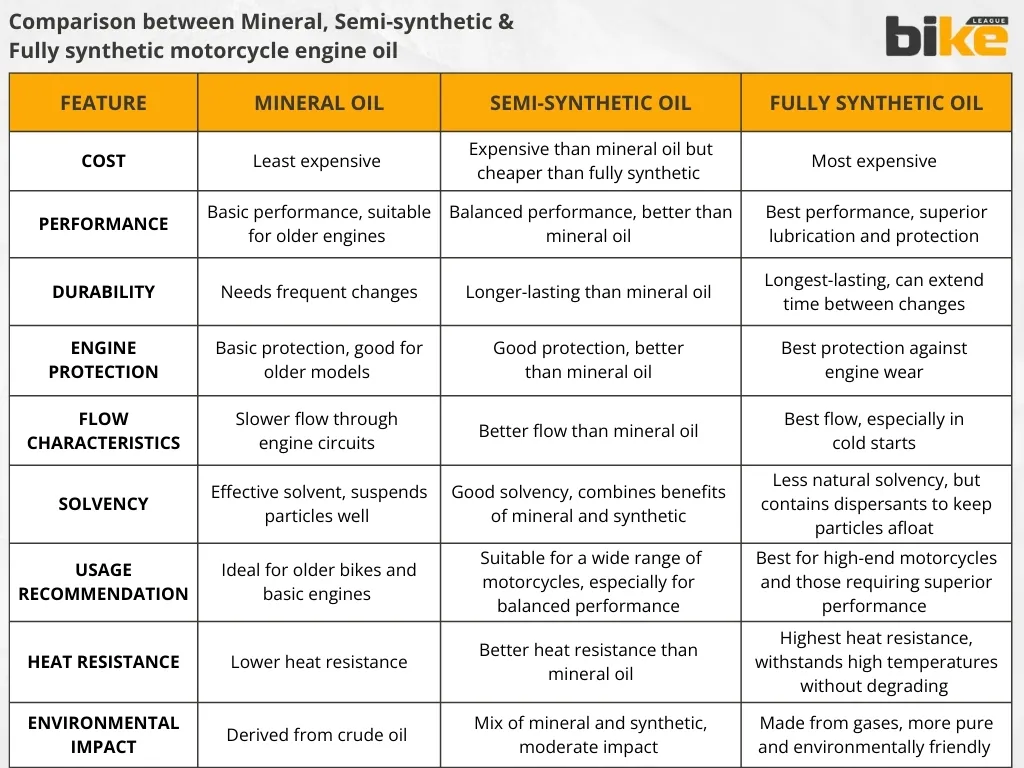
Comparison of different types of motorcycle engine oil – Table
The table below compares the three main types of motorcycle engine oil in India—mineral, semi-synthetic, and fully synthetic—showing their main features and common uses.
| Feature | Mineral Oil | Semi-Synthetic Oil | Fully Synthetic Oil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Refined from crude oil | Blend of mineral + synthetic | Chemically engineered synthetic |
| Cost | Least expensive | Moderately priced | Most expensive |
| Viscosity Stability | Lower, breaks down faster | Better than mineral | Excellent, stable across temperatures |
| Engine Protection | Basic protection | Good protection with additives | Superior protection, reduces wear |
| Heat Resistance | Suitable for low/moderate heat | Better heat resistance | Excellent thermal & oxidation resistance |
| Change Interval | Shorter (2,000–2,500 km) | Moderate (3,000–4,000 km) | Longest (4,000–6,000+ km) |
| Suitable Bike Types | Entry-level/commuters (100–125cc) | Mid-capacity (125–200cc), mixed use | High-performance & premium bikes (180cc+) |
| Performance | Basic, for daily city riding | Balanced mileage & performance | Best smoothness, power & mileage gain |
| Additives | Limited | Contains detergents, anti-wear | Advanced additive packages |
What specific intervals should I follow for changing the oil based on my motorcycle type and oil types in India?
How often you should change your motorcycle’s oil in India depends on your bike’s engine size, how you use it, and the type of oil you use—mineral, semi-synthetic, or fully synthetic.
| Motorcycle Type | Oil Type | Change Interval (km) | Time Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100–125cc commuter | Mineral | 2,000–2,500 | 6 months |
| 100–125cc commuter | Semi-synthetic | 3,000 | 6 months |
| 100–125cc commuter | Synthetic | 4,000–5,000 | 12 months |
| 150–200cc mid-range | Mineral | 2,500–3,000 | 6 months |
| 150–200cc mid-range | Semi-synthetic | 3,500–4,000 | 6–12 months |
| 150–200cc mid-range | Synthetic | 5,000–6,000 | 12 months |
| 250cc+ performance | Mineral | 3,000 | 6 months |
| 250cc+ performance | Semi-synthetic | 5,000 | 12 months |
| 250cc+ performance | Synthetic | 6,000 | 12 months |
| Scooters 90–125cc | Mineral | 2,000 | 6 months |
- If riding in harsh conditions, heavy traffic, or hot climates, reduce the interval by 20–30%.
- Always follow manufacturer guidelines in the owner’s manual for best results; these override general intervals.
- Choose the highest-grade oil allowed by the manufacturer for longer intervals and better performance.
What are the key considerations for choosing bike engine oil?
1. Manufacturer Recommendations
Refer to your motorcycle’s owner’s manual for the manufacturer-recommended oil grade and type. Using the specified oil ensures optimal engine performance and longevity.
2. Riding Conditions
You should also think about your riding conditions when choosing engine oil. Some oils handle very hot or cold weather better because they stay stable and flow well in extreme temperatures.
3. Oil Change Intervals
Changing your oil regularly keeps your engine healthy. Most bikes need an oil change every 5,000 kilometres, but fully synthetic oils can last 7,000 to 10,000 kilometres. Always check the oil’s colour—if it turns black, it’s time to change it.
Which are some of the best bike engine oil brands?
Here, we are not recommending individual engine oil because engine oil type varies among models, but instead, we are suggesting some of the best brands, and they are
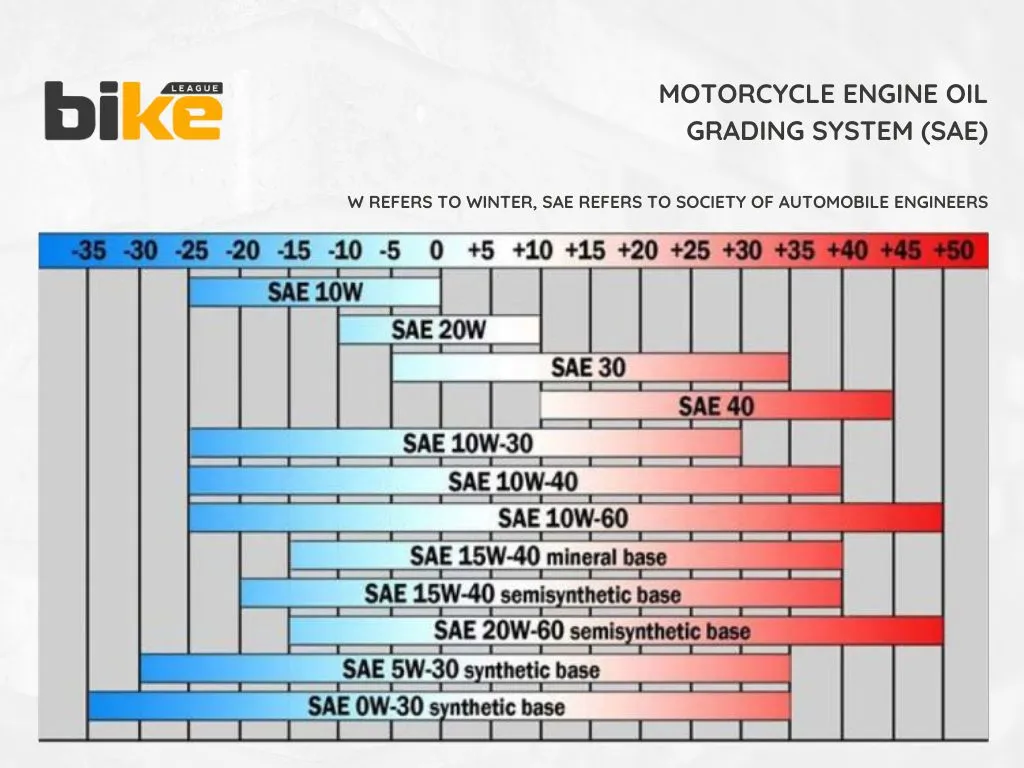
How to read motorcycle engine oil grade?
The name SAE number also refers to the engine oil grade code. SAE refers to the Society of Automotive Engineers. The letter W refers to ‘Winter’ in the code. The first number refers to how oil flows when cold, such as during engine start-up. The second number is defined by how oil flows at higher temperatures than those of a standard engine operating temperature.
Thin, low-viscosity oils flow more easily to protect engine parts at cold temperatures. Thick, high-viscosity oils are typically more effective at maintaining film strength, which protects engines at high temperatures. For example, a 5W-20 will flow more effortlessly than a 10W-20 at start-up temperatures, and a 10W-40 will flow more effortlessly than a 10W-50 at regular engine operating temperatures.
The chart below recommends engine oil based on the outside temperatures.
Does motorcycle engine oil expire?
Yes, motorcycle engine oil does expire, but not as quickly as food. The date on the container is a guideline, so it’s best to use the oil within that time. Here’s what you should know about oil expiration:
Unopened Oil
- Conventional oil: Generally has a shelf life of 2-5 years.
- Synthetic oil: Can last up to 10 years when stored unopened in a cool, dry place.
Opened Oil
- Once the container is opened, the oil degrades due to exposure to air and moisture.
- It’s recommended to use opened oil within 1-2 years.
How to change motorcycle engine oil?
You should change your bike’s engine oil as your owner’s manual suggests. The manual gives step-by-step instructions, and you can do it at home if you have the right tools. Make sure your bike is on its centre stand, or use a paddock stand if needed.
The general steps for a bike engine oil change are as follows:
- Warm up the engine: Run the motorcycle for 5-10 minutes to warm the oil. Warm oil drains faster and more completely.
- Prepare the workspace: Park the bike on a level surface, use the centre stand or paddock stand to keep it upright and stable. Gather the necessary tools, including a wrench/spanner, drain pan, funnel, gloves, and fresh engine oil.
- Locate the drain plug and oil filter: Refer to the owner’s manual for exact locations. Typically, the drain plug is located at the bottom of the engine crankcase. At the same time, the oil filter is positioned on the side.
- Drain old oil: Place the drain pan under the drain plug. Loosen and remove the plug carefully, allowing the oil to drain out fully. Be cautious as the oil might be hot.
- Remove and replace oil filter (if applicable): Unscrew the oil filter using an oil filter wrench or by hand (refer to manual). Replace the filter with a new one, lubricating the new filter’s rubber seal with a small amount of fresh oil before installation.
- Reinstall drain plug: Clean the drain plug and gasket/seal ring. Screw it back securely, but avoid overtightening to prevent stripping the threads.
- Add fresh oil: Using a funnel, pour the recommended quantity and grade of fresh engine oil into the oil filler cap opening. Check the owner’s manual for the correct oil type and quantity.
- Check oil level: Use the dipstick or sight glass to confirm oil level is within the recommended range. Add more if necessary.
- Run the engine and check for leaks: Start the motorcycle and let it idle for a few minutes. Check the drain plug and filter for any leaks.
- Dispose of old oil properly: Collect used oil in a sealed container and take it to authorised disposal or recycling centres.
Are there any signs that indicate the need for an oil change before the six-month mark in a motorcycle in India?
Yes, there are specific signs that indicate a need for a motorcycle oil change before the usual six-month mark in India:
- Dark, thick, or blackened oil: Engine oil that has turned very dark or has sludge deposits shows degradation and poor lubrication, signalling immediate replacement.
- Low oil level: A noticeable drop in oil volume on the dipstick or sight glass requires topping up or changing the oil if it occurs frequently.
- Unusual engine noises or vibrations: Increased engine noise, rough clutch operation, or vibrations often mean poor lubrication and oil breakdown.
- Engine overheating: Feeling excessive heat on legs or bike parts due to ineffective oil heat dissipation indicates the oil is losing its properties.
- Reduced throttle response or power: The engine may feel less responsive or sluggish, an indirect sign that the oil is unable to maintain optimal performance.
- Burning smell: A distinct burning oil smell during riding indicates oil degradation or leakage.
- Oil warning light or dashboard alerts: Some motorcycles have sensors to alert to low oil pressure or quality issues.
- High-stress riding conditions: Frequent city traffic, high heat, dusty roads, and excessive idling can accelerate oil degradation and require earlier changes.
- First service oil change: For new motorcycles, the first oil change is often recommended between 500–700 km to remove break-in contaminants, regardless of time.
Checking the oil regularly for color, level, and consistency, and being alert to these signs, ensures timely oil changes that protect engine health and prevent costly damage.
FAQ related to bike engine oil
1. What are the functions of bike engine oil?
Engine oil functions to minimise friction, reduce wear, clean the engine, improve engine parts, form a seal, dampen shock, and prevent corrosion.
2. What is an engine oil grade?
Engine oil grade refers to a set of specifications or codes that correspond to the type of engine oil. It primarily describes the type of engine oil used, taking into account external environmental conditions. More technically, engine oil grade refers to the viscosity or resistance to flow. The lower the number, the better it will flow.
3. When to change motorcycle engine oil?
Engine oil must be changed every 2,500-3,000 miles or every six months, depending on the type of engine oil. Synthetic and semi-synthetic oils last longer, so ask a bike technician or shop owner for the same. In the case of mineral oil, oil replacement is recommended every 2000-3000. Anyway, an oil change is mandatory every six months, regardless of any other factors.
4. What happens when the engine oil change is late?
A delay in engine oil change results in performance loss and a drop in fuel efficiency. Overall, it affects the engine’s life and the vehicle’s performance.
5. How to Check for Bike Oil Replacement?
Check the oil colour by loosening the engine oil bolt and allowing oil to drip into the oil pan. This method varies among models, and alternative methods are available for some models. If the colour is dark, it is time for an oil replacement. Brand-new engine oil is always clear and almost transparent.
6. Is it mandatory to change the oil filter while changing the oil?
Yes, when you change the engine oil, it’s also a good idea to replace the oil filter. An oil filter protects the engine from potential damage by removing contaminants that can accumulate in the motor oil. Like engine oil, your bike’s oil filter becomes clogged or damaged after a specific period. Change the engine oil filter once a year or after every two general services. Check the owner’s manual for this information.
7. What is a bike engine flush?
An engine flush is an aftermarket chemical additive that cleans accumulated engine sludge and deposits.
8. How to flush the motorcycle engine or engine oil?
Add the engine oil flush to the crankcase before the regular oil change. An oil flush cleans the interior parts of the engine from sludge and grease deposits, leaving them fresh for new lubrication.
9. What is the recommended engine oil quantity for the motorcycle?
For that, check the owner’s manual. The quantity of oil should neither be excessive nor insufficient; service manual guidelines must be strictly followed. As the owner’s manual mentioned, the oil quantity should be higher when changing the filter. The last point is critical to note.
10. Should the bike engine be warm while changing the oil?
Yes. The engine oil is thicker and colder during the early morning hours. To loosen the oil, drive the motorcycle or warm the engine for a short time.
11. Does motorcycle engine oil burn?
Yes. Suppose an issue exists within the engine components, like piston rings. In that case, oil deposits can accumulate on the engine spark plugs or the valve bottoms. That means the oil enters the combustion chamber and burns away.
12. How to fix an oil leak in a motorcycle?
A motorcycle engine oil leak is not a DIY task and should be handled by a technician. If an engine oil leak is present, turn off the motorcycle immediately and inform the technician. Coordinate the remaining steps with the technician. Nowadays, several companies offer roadside assistance, such as Royal Enfield, which is a great initiative.
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Bike maintenance at home: Save money & time on services
- Second hand motorcycle: Things to know when buying It
- Diesel Wash For Bike: Is It Good or Bad
- Motorcycle service – All things you need to know explained
- SVM
Conclusion
We’ve covered the main topics about bike engine oil and its types in this article. If you have more questions, feel free to email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com or leave a comment below. We’re always happy to help. You can also connect with us on our social media pages.