Long story short: In this discussion, we will explore the different types of motorcycle suspension, including front and rear systems, various suspension types, maintenance advice, and frequently asked questions.
Motorcycle suspension keeps your ride stable and comfortable, particularly on rough or unpaved surfaces. In India, where many roads are uneven, effective suspension makes a noticeable difference in ride quality.
When picking a bike, it’s essential to consider its suspension. Good suspension helps with handling, braking, safety, and comfort. We’ll explain the main types of front and rear suspension, share maintenance tips, and answer common questions. Let’s start by looking at the main categories of motorcycle suspension.
Key Takeaways
- USD forks are an improved version of telescopic forks. They use inverted tubes, which help make the bike lighter and handle better. Many riders choose USD forks for these reasons.
- Mono-shocks use a single shock absorber placed in the centre, often below the seat. This type connects the rear swingarm to the frame. It helps distribute weight more evenly, improving how the motorcycle handles.
- Dual shock absorber systems use two shock absorbers at the rear of the motorcycle. This spring-loaded hydraulic suspension is common in cruisers and touring bikes.
- Gas-filled shocks use gas, usually nitrogen, to improve how well they absorb bumps. The gas keeps damping steadily by reducing cavitation. Cavitation is when air bubbles form in the damper, making it less effective at controlling movement.
- In most motorcycles, there is an option to adjust the motorcycle suspension to a softer or harder suspension feel in the rear section. There will be a nut or a screw for the same to adjust. For detailed instructions, please refer to the owner’s manual.
Different types of motorcycle suspension
Motorcycle suspension can be categorised into two:
- Front motorcycle suspension setup
- Rear motorcycle suspension setup
In this, for each setup, there are different types, and they are
Different types of front motorcycle suspension
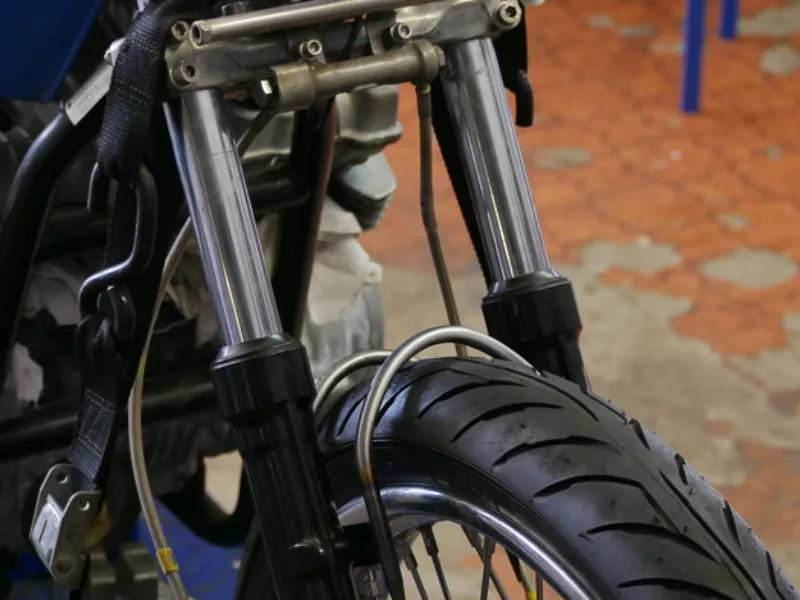
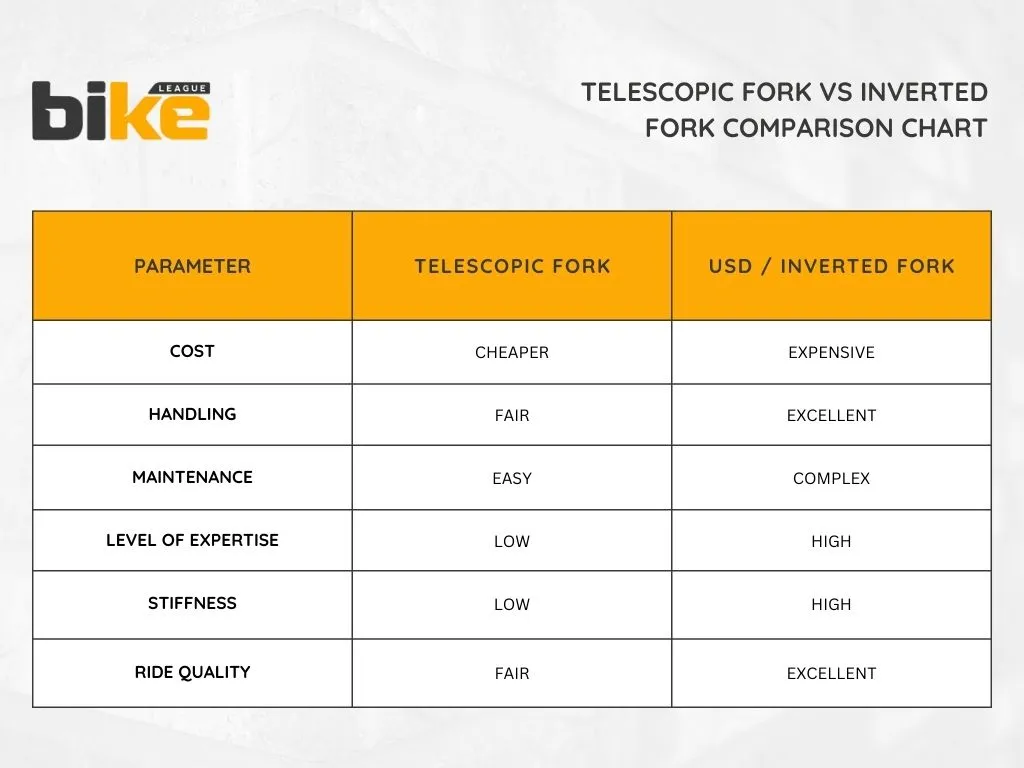
1. Telescopic forks
These forks are the most common front suspension system. They use two fork tubes, containing springs and dampers. When the front wheel hits a bump, the tubes compress. The springs and dampers absorb the shock to soften the impact.
Pros of telescopic forks
- Simplicity and ease of maintenance
- Less expensive
Cons of telescopic forks
- Low level of stiffness compared to USD forks
- Low precision level compared to USD forks
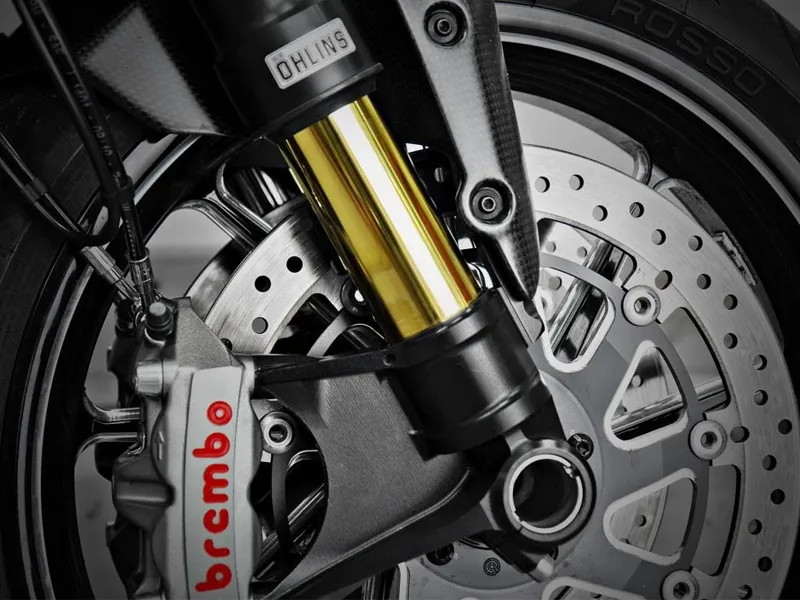
2. Upside-down telescopic forks (USD) or inverted forks
USD forks are an improved version of telescopic forks. They use inverted tubes, which help make the bike lighter and handle better. Many riders choose USD forks for these reasons.
Pros of Upside-down forks
- High level of stiffness compared to telescopic forks
- High precision level compared to telescopic forks
- Better handling compared to telescopic forks
Cons of Upside-down forks
- Expensive
- Tough to repair if an oil leak is there
- Need extra care and maintenance
Different types of rear motorcycle suspension
1. Spring-loaded hydraulic suspension
Among rear motorcycle suspension types, this system uses springs and hydraulic dampers to absorb shocks from the rear wheel. Springs are elastic metal coils that compress to absorb bumps. Hydraulic dampers use oil to slow and control the spring’s movement. Together, they provide a smoother ride over uneven roads.
Pros of Spring-loaded hydraulic suspension
- Good for absorbing large bumps, adjustable preload and damping
Cons of Spring-loaded hydraulic suspension
- Can be heavy, requires regular maintenance
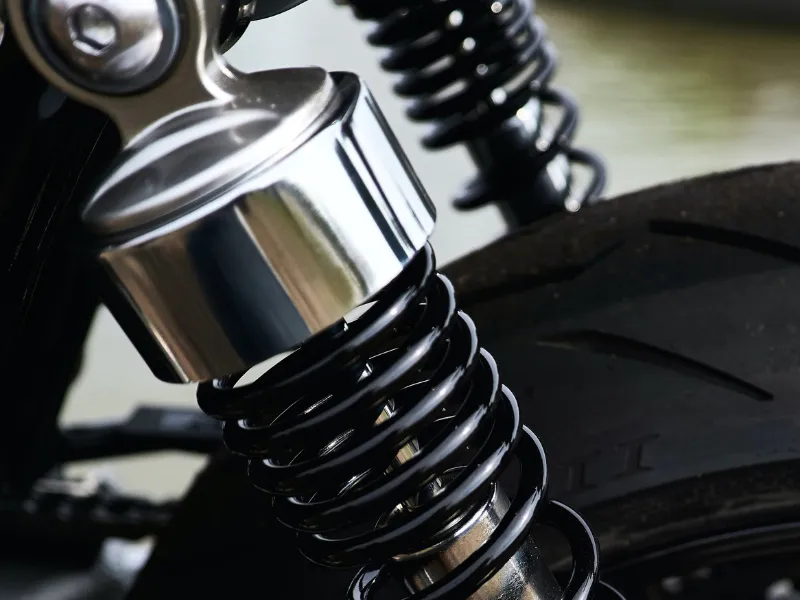
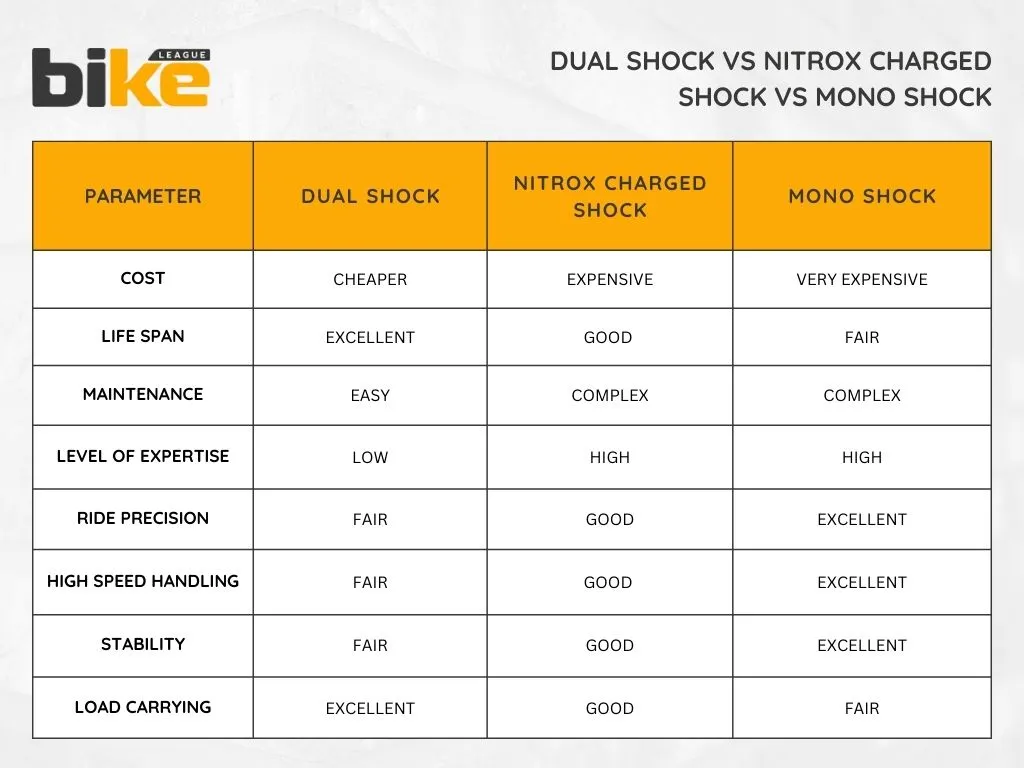
2. Dual or Twin shock absorber suspension
Dual shock absorber systems use two shock absorbers at the rear of the motorcycle. This spring-loaded hydraulic suspension is standard in cruisers and touring bikes. Both shocks work together to absorb impacts from the rear wheel.
Pros of twin shock absorber suspension
- Easier to maintain
- Offers a supple ride
- Cost-effective
Cons of twin shock absorber suspension
- Variable damping from two shocks as they work independently
- It offers less stability while cornering
- It offers less stability at high speeds
- In extreme conditions, damping oil may form bubbles (cavitation), affecting damping performance.
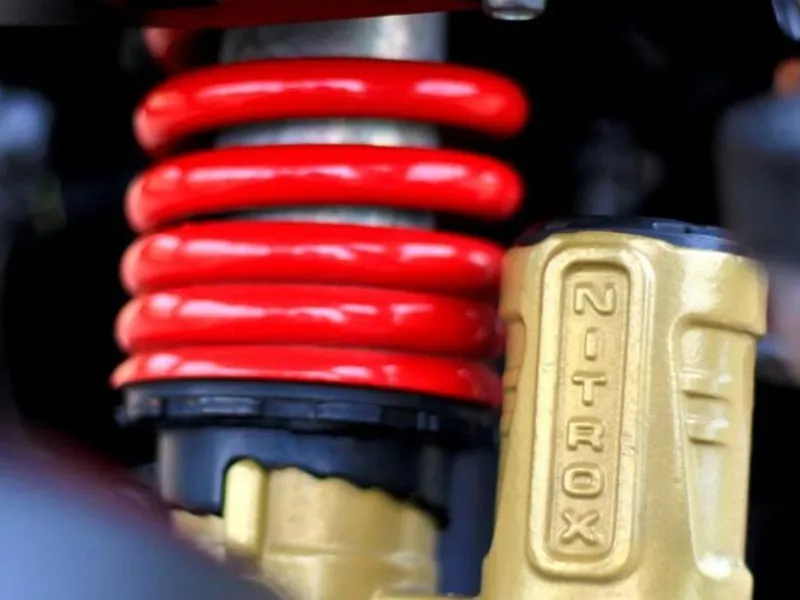
3. Gas-filled or Nitrox-charged shock absorber
These shocks use gas, usually nitrogen, to improve how well they absorb bumps. The gas keeps damping steadily by reducing cavitation. Cavitation is when air bubbles form in the damper, making it less effective at controlling movement.
Pros of Nitrox charged shock absorber
- Prevents cavitation issues
- Reduced bouncing on irregular surfaces
- Efficient dissipation of heat on the tube
- Offers better stability in corners and at high speeds
Cons of Nitrox charged shock absorber
- Expensive than a twin shock absorber
- Complicated with repair and maintenance
4. Mono shock absorber
Mono-shocks use a single shock absorber placed in the centre, often below the seat. This type connects the rear swingarm to the frame. It helps distribute weight more evenly, improving how the motorcycle handles. Mono-shock setups offer stability and better control over bumps.
Pros of mono shock absorber suspension
- Superb cornering capability and handling
- Excellent high-speed stability and rideability
- Easy to tune and adjust
- Precise damping
Cons of mono shock absorber suspension
- High maintenance
- Cannot carry the excess load
- Shorter life span compared to other suspension setups
- Expensive
How does riding style affect the choice of suspension type in motorcycles in India?
Riding style influences the ideal suspension type in motorcycles, especially in India’s diverse road conditions. Suspension choice affects how well a motorcycle balances comfort, control, and durability based on where and how it’s ridden.
1. Commuting and City Riding
Daily city riders on Indian roads with potholes and speed bumps are best served by telescopic front forks and twin rear shock absorbers. This combination delivers simplicity, affordability, and effective damping for stop‑and‑go traffic.
Examples include models like the Hero Splendor Plus and Honda Shine, which feature hydraulic telescopic front suspension and five-step adjustable rear shocks to enhance comfort in congested areas.
2. Touring and Highway Riding
Touring motorcycles such as the Bajaj Dominar 400 and Yamaha FZ25 are fitted with monoshock rear suspension combined with telescopic or USD forks.
This design improves cornering stability at high speeds and maintains consistent handling under heavy luggage. Adjustable preload helps manage extra load from panniers or a pillion on long trips, making monoshocks ideal for extended Indian highway rides.
3. Sport and Performance Riding
Sport riders who prefer aggressive cornering and track‑level handling need stiffer, performance‑oriented suspensions. Upside‑down (USD) forks in the front and gas‑charged or nitrogen monoshocks in the rear are standard.
This setup minimises fork dive under braking and improves precision at high speeds. Bikes like the KTM Duke 200 and Bajaj Pulsar NS200 feature this combination to deliver sharper handling.
4. Off‑Road and Adventure Riding
Adventure and off‑road riders require long‑travel suspension systems with higher ground clearance. Bikes such as the Hero Xpulse 200 4V and Royal Enfield Himalayan use a long‑stroke telescopic or USD fork paired with a monoshock rear.
These systems are tuned for softer damping, allowing better absorption of terrain irregularities and superior traction during trail rides.
5. Cruiser and Comfort‑Focused Riding
Cruisers like those from Royal Enfield or Harley‑Davidson rely on dual rear shock absorbers tuned for a plush, laid‑back experience.
Some premium cruisers use Softail‑type suspension where shocks are hidden inside the frame, offering both comfort and style for relaxed long‑distance cruising.
| Riding Style | Suspension Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| City commuting | Telescopic + Dual shocks | Comfort, low upkeep, affordable |
| Touring / highway | Telescopic / USD + Monoshock | Load adaptability, stability |
| Performance / sport | USD forks + Monoshock | Precision handling, reduced dive |
| Off-road / adventure | Long-travel telescopic + Monoshock | Terrain absorption, traction |
| Cruiser / relaxed | Dual shock or Softail | Plush comfort, aesthetic balance |
What are the signs that indicate a motorcycle’s suspension needs repair or adjustment in India?
A motorcycle’s suspension system gives comfort, road grip, and control. In India’s riding conditions—with potholes, speed breakers, and uneven roads—diagnosing early suspension issues is critical to safety. Here are clear signs that your motorcycle suspension likely needs repair or adjustment.
1. Extra Bumpy or Harsh Ride
Suppose your motorcycle suddenly feels bumpier than usual or transmits vibrations even on mild irregularities. In that case, the suspension may no longer absorb shocks efficiently. This often happens due to worn-out springs or leaking shock absorber oil.
2. Oil Leaks or Greasy Residue
Visible oil or grease around the front forks or rear shock absorber is a significant indicator of seal failure or internal damage. Dirt sticking to these oily spots is another visual clue that damping performance has been compromised and needs immediate service.
3. Unusual Sounds and Noises
Thudding, clunking, or rattling noises when riding over bumps or rough patches suggest loose, broken, or worn suspension components. These noises often worsen over time and can lead to further mechanical failures if ignored.
4. Difficulty in Handling or Cornering
If your bike feels unstable when cornering, braking, or riding at high speed—especially if it wobbles or “floats”—it indicates poor damping, misalignment, or excess suspension softness. This can become dangerous during emergency manoeuvres.
5. Uneven Tyre Wear
Worn-out shocks or improper suspension alignment can cause the tyres to wear unevenly. Inspect tread patterns regularly: cupping or irregular marks, especially on the front tyre, signal a suspension imbalance that requires professional attention.
6. Longer Braking Distances
Suppose your motorcycle takes longer to stop, even with properly working brakes. In that case, the suspension may have lost its ability to stabilise the bike during deceleration. This can increase stopping distance and should be checked immediately.
7. Excessive Bouncing or Sagging
When the bike keeps bouncing after hitting a bump, or if it noticeably “sags” lower when you sit on it, the springs or dampers have likely worn out. Suspension sag adjustment or part replacement may be needed.
8. Visible Damage or Stiffness
Cracks, rust on fork tubes, or stiffness during compression are direct signs of trouble. In India’s humid or dusty conditions, corrosion and seal wear are common and should not be overlooked.
FAQ related to different types of motorcycle suspension
1. How does motorcycle suspension work?
Motorcycle suspension combines a spring, which absorbs bumps and shocks, and a shock absorber, also called a damper, which reduces and controls the bouncing motion caused by the spring. An effective suspension setup needs these two parts and enough room (range of motion) to allow movement. The damper slows the spring’s bounce, making rides smoother and more stable.
2. How can we adjust motorcycle suspension?
In most motorcycles, there is an option to adjust the motorcycle suspension to a softer or harder suspension feel in the rear section. There will be a nut or a screw for the same to adjust. For detailed instructions, please refer to the owner’s manual.
3. How can we adjust motorcycle suspension according to weight?
This is not a DIY task and requires expertise.
4. Which is the best motorcycle suspension setup for performance-oriented bikes?
In the front section, go for USD forks, while in the rear, mono shocks are the best. It is a significant performance bonus if mono-shock comes with a gas canister.
5. Which motorcycle suspension setup is best for heavy riders and loads?
Go for dual shock absorbers with gas canisters in the rear. At the same time, in the front section, both setups, telescopic and inverted forks, are acceptable.
6. When to change and repair the two-wheeler suspension?
In 99% of cases, suspension change is not required other than in significant accidents. However, a regular shift in the fork or damping oil is needed as per the service manual.
7. What is Preload on motorcycle suspension?
It refers to the initial position of suspension with the motorcycle’s weight and rider acting on it.
8. What is Rebound on two-wheeler suspension?
Rebound is the rate at which the suspension can extend and return to its normal position once the motorcycle has encountered a bump.
9. What is Brake dive on motorcycle suspension?
When the brakes are applied, the front wheel causes the bike’s front end to go lower, resulting in the compression of the forks, known as brake dive.
10. What is damping on a two-wheeler suspension?
Damping controls or stops the spring’s oscillation when it compresses or rebounds.
11. What is motorcycle suspension sag?
Suspension sag is the amount of suspension travel used when sitting on your bike in a natural riding position.
12. What is a soft suspension setup?
Soft suspension gives the vehicle a plush, low-speed ride and is not rigid. Even when the road gets rough, the ride will not be uncomfortable. This suspension is ideal for commuting but is not recommended for high-speed and enthusiastic riders.
13. What is a hard suspension setup?
A complex suspension setup is the exact opposite of a soft suspension setup. This setup is recommended for high-speed and enthusiastic riders, where the handling is excellent. The downside of this setup is that the rider can feel all bumps and irregularities on the road.
14. What is a medium suspension setup?
A medium suspension setup sits between a soft and a firm one. It provides a good balance of ride and handling. It gives the best of both worlds of soft and hard suspension setups.
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Motorcycle chain – how to clean, adjust & maintain
- Motorcycle riding style – How to choose your perfect bike
- Two wheeler tyres – Different types, pros & cons
- Ducati Supersport 950 S
- Ducati Supersport 950
Conclusion
We’ve covered the main types of motorcycle suspension, their pros and cons, and answered some common questions. If you have more questions, feel free to email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com or leave a comment below. We’re here to help. You can also connect with Bikeleague India on our social media platforms.