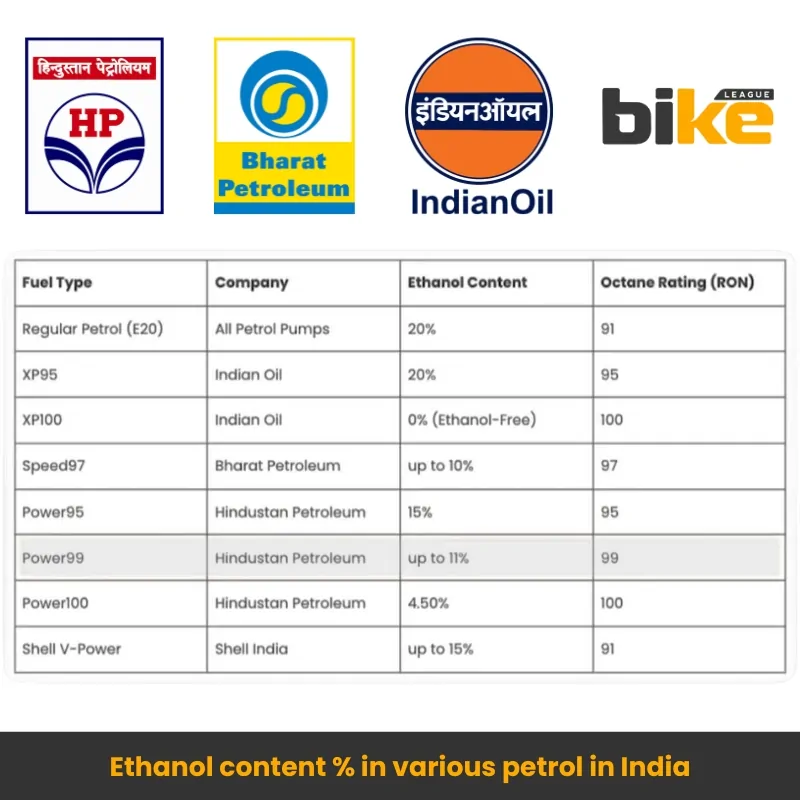
Long story short: Here’s a quick guide to ethanol petrol blending in India. Learn about the benefits of E10 and E20 fuels and how they are helping motorcycles become more eco-friendly.
Key Takeaways
- Widespread Adoption and Policy Drive: India’s Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme has quickly advanced from E5 (5% ethanol) to E10 (10% ethanol, now standard nationwide) and is moving towards E20 (20% ethanol) by 2026. This progress is driven by government policies for cleaner fuels and greater energy security.
- Environmental and Economic Benefits: Ethanol blends help cut harmful emissions and promote energy independence by reducing crude oil imports. They also support the agricultural sector by creating new markets for crops like sugarcane and corn,which benefits rural communities.
- Vehicle Compatibility and Maintenance: Most modern motorcyclescan use E10 without any changes. However,g E20 or higher blends require engines and fuel systems made with ethanol-resistant materials. Using these fuels in non-compatible bikes can lead to more wear and tear, higher maintenance costs, and the risk of voiding the warranty.
- Cost and Efficiency Considerations: E10 and E20 may reduce fuel efficiency slightly (by 2–7%), but government subsidies and competitive pricing often make up for it. For motorcycles not built for E20, long-term costs can be much higher due to more frequent repairs and part replacements.
- Changes for Manufacturers and Suppliers: Motorcycle and part manufacturers are investing in new engine designs, materials, and quality standards to ensure ethanol compatibility. While this shift is driving innovation, it’s also raising production costs and increasing the need for customer education.
What is ethanol?
Ethanol is a clear, colourless alcohol made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (C2H5OH). It has a strong, easily recognised smell and taste.
Pure ethanol is non-toxic and breaks down naturally, but fuel-grade ethanol is treated to prevent its consumption.
What is ethanol blended petrol?
Regular petrol is pure petrol. E10 fuel, now available in India for motorcycles, contains 10% ethanol, an alcohol derived from plants like sugarcane.
What is the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme?
The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme began in January 2003 to promote using petrol mixed with ethanol instead of regular petrol. The main aims are to boost energy security, reduce climate change, and help farmers.
Types of ethanol-blended petrol in India.
Over the last 10 years, ethanol-blended petrol in India has changed significantly. The government’s EBP Programme set clear goals and blended types to cut crude oil use and reduce vehicle emissions.
1. E5 (5% ethanol blend)
- Initially introduced as an entry-level ethanol blend to begin the blending program.
- Compatible with most vehicles, but largely a starting point in blending targets.
2. E10 (10% ethanol blend)
- Became the default blend at petrol stations nationwide by the early 2020s.
- Compatible with most existing petrol vehicles without requiring engine modifications.
- Adoption accelerated under government mandates, and blending targets were achieved around 2022-2023.
3. E20 (20% ethanol blend)
- Currently being rolled out on a larger scale since around 2024-2025.
- E20-compatible vehicles are built to run on petrol with 20% ethanol without engine problems. Flex-fuel technology lets an engine use more than one type of fuel, like E20 or higher ethanol blends.
- The government aims for nationwide availability by 2026.
4. Higher blends like E85
- Used for flex-fuel vehicles with up to 85% ethanol content.
- E85 is mostly used in flex-fuel vehicles and is not yet commonly available for motorcycles in India; it is still being discussed at the policy or pilot-testing stage.
Making of ethanol
Ethanol is mainly made from renewable sources like corn, sugarcane, barley, and wheat. It can also come from plant leftovers and wood.
Pros of Ethanol Blended Petrol
- Reduced Emissions: Ethanol burns cleaner than gasoline, releasing less carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and soot and potentially improving urban air quality.
- Renewable Resource: Ethanol can be made from renewable plants like corn and sugarcane, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: Using ethanol reduces reliance on imported oil, helping to improve national energy independence.
- Improved Engine Performance: Ethanol’s higher octane rating improves performance and reduces knocking.
- Rural Development: Producing ethanol generates rural jobs and supports local agricultural economies.
E20 has many benefits, but it also brings challenges for riders and manufacturers. These include ensuring vehicles are compatible, covering higher infrastructure costs, addressing potential corrosion and moisture, and managing the environmental impacts of increased farming.
Cons of Ethanol Blended Petrol
- Not Compatible with All Bikes: Higher ethanol blends (E85) may not suit all bikes and can damage older engines.
- Infrastructure expenses: Expanding ethanol use means extra investment in storage, pumps, and distribution systems for E20.
- Corrosive nature: Ethanol absorbs moisture from the air, which can cause phase separation and corrosion if not managed.
- Water absorption: Agricultural practices for producing ethanol, such as intensive farming, can cause issues like soil erosion, pesticide use, and deforestation.
- Environmental impact of agriculture: The intensive farming practices involved in ethanol production can contribute to environmental issues like soil erosion, pesticide usage, and deforestation.
Using sustainable farming methods can help reduce these problems.
What is the impact of ethanol-blended petrol on the motorcycle owner in India?
Motorcycle owners in India notice the effects of ethanol-blended petrol in areas like fuel economy, maintenance, performance, costs, and the environment.
1. Fuel Economy and Cost
- Ethanol has about 30% less energy than pure petrol, so motorcycles might get slightly lower fuel efficiency (kilometres per litre) when using E10 or higher blends.
- However, ethanol-blended fuel is often priced competitively or receives government subsidies. This can help offset the lower efficiency, so the cost per kilometre is sometimes the same or even lower than with regular petrol.
2. Maintenance Considerations
- Bikes that aren’t designed for higher ethanol blends above E10 may need more frequent checks for fuel leaks or worn parts, as ethanol can affect some materials.
- Motorcycles that use E10 usually don’t need extra maintenance. For higher blends like E20, it’s important to have ethanol-resistant fuel systems to keep the bike running well over time.
3. Performance and Ride Experience
- Modern motorcycles with fuel injection and engine management systems made for ethanol blends usually keep good power and throttle response with E10. Some riders might even notice a slight improvement in throttle response, as ethanol has a high octane rating.
- Older or carbureted bikes using higher ethanol blends may hesitate, lose power, or idle roughly unless they are adjusted.
4. Environmental and Social Benefits
- Using ethanol blends helps reduce harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter. This leads to better air quality in cities, especially in many Indian cities where motorcycles are common.
- Ethanol blending helps India’s energy security goals. It also encourages the use of local biofuels and gives farmers a chance to earn more by producing ethanol.
5. Warranty and Compliance
- Motorcycle owners should check if their bikes are certified for the ethanol blend they use. Using E20 or higher in bikes that aren’t made for it can void the warranty or damage the engine.
- Manufacturers and oil companies work to educate customers about which fuels are right for their vehicles and encourage the use of the correct ethanol blends.
| Impact Aspect | Effect | Advice/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel efficiency | Slight decrease with higher ethanol blends | Cost offset by ethanol price subsidies |
| Maintenance | Minimal for E10; more frequent checks with E20+ | Use ethanol-resistant components for high blends |
| Performance | Generally good with E10; needs tuning for E20+ | EFI bikes cope better than carbureted |
| Environmental | Lower emissions, better air quality | Supports sustainability goals |
| Warranty | Use compatible blends to avoid warranty issues | Check manufacturer recommendations |
What is the impact of ethanol-blended petrol on the motorcycle manufacturer in India?
For motorcycle makers in India, ethanol-blended petrol is a game-changer. It affects how bikes are designed, built, and sold, as well as what customers expect on the road.
1. Engine and Fuel System Design
- Manufacturers must design or adapt engines and fuel-delivery systems to be compatible with ethanol blends, especially when moving from E10 to E20 or higher blends.
- Ethanol’s properties require ethanol-resistant parts in the fuel system to prevent wear and damage.
- Engine calibration must account for ethanol’s properties to achieve efficient, durable performance.
2. Compliance with Emission Norms
- Ethanol blends help manufacturers meet increasingly stringent Bharat Stage (BS6 and beyond) emissions standards by reducing carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and particulate emissions.
- Use of ethanol blends necessitates testing and certification for vehicles on E10 and E20 fuels, increasing developmental and homologation costs but providing a cleaner emissions profile.
3. Manufacturing and Cost Implications
- Production costs may rise due to the need for upgraded materials and electronics to handle ethanol blends, as well as compliance testing expenses.
- Some manufacturers invest in flex-fuel technology capable of handling a wide range of ethanol blends (up to E85) to future-proof models for evolving fuel policies and customer needs.
- Development of such technology requires capital investment but can create competitive differentiation in a shifting market.
4. Supply Chain and Market Strategy
- Manufacturers align product launches with fuel availability, introducing E20-compatible motorcycles initially in states or cities with E20 infrastructure.
- They educate dealerships and customers on the benefits and limitations of ethanol-blended fuels, including warranty conditions and recommended fuel types.
- Strategies include tailoring engine tuning and marketing to leverage ethanol’s octane benefits, thereby improving throttle response and reducing emissions.
5. Environmental and Regulatory Alignment
- Adoption of ethanol-compatible vehicles positions manufacturers as contributors to the government’s clean air and energy security goals, supporting sustainability credentials.
- Compliance with ethanol fuel regulations and standards is mandatory, impacting product planning and regulatory approvals for domestic and export models.
| Aspect | Impact | Manufacturer Response |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Design | Requires ethanol-resistant materials and calibration | Redesign or adapt engines/fuel systems |
| Emission Compliance | Facilitates meeting stricter BS emission norms | Conduct testing and certification for ethanol blends |
| Cost | Increased production and development costs | Invest in technology; adjust pricing and product strategy |
| Market Strategy | Align products with regional fuel availability | Target launches; educate dealers and consumers |
| Environmental Roles | Aligns with clean fuel policies | Leverage sustainability for brand positioning |
What is the impact of ethanol-blended petrol on the component manufacturer in India?
Ethanol-blended petrol (EBP) has a big impact on motorcycle component makers in India. It affects the materials they use, how they produce parts, quality standards, and new product development.
1. Materials and Component Design
- Ethanol’s solvent and hygroscopic (water-absorbing) nature requires component manufacturers to switch to ethanol-resistant materials for fuel system parts such as fuel tanks, fuel lines, gaskets, seals, carburettors, injectors, and filters.
- Components must resist corrosion, swelling, and degradation caused by ethanol and moisture to maintain durability and reliability, prompting innovations in polymers, elastomers, and coatings.
2. Production and Quality Standards
- Manufacturers face tighter quality-control standards to ensure components withstand ethanol’s chemical properties throughout the product lifecycle.
- Testing protocols are enhanced to simulate long-term exposure to ethanol blends (up to E20 or higher), accelerating quality assurance and certification requirements.
- Compliance with updated Indian and international standards (BIS, ISO) related to ethanol compatibility influences production processes and supplier audits.
3. Supply Chain Adaptation
- Component suppliers adjust sourcing and inventory to prioritise ethanol-compatible raw materials and chemicals.
- Collaboration with motorcycle OEMs and fuel suppliers intensifies to align on specifications and innovation roadmaps, aiming at ethanol-ready systems.
- Investments in R&D and pilot manufacturing for new ethanol-compatible components increase to meet growing market demand.
4. Cost and Market Dynamics
- The use of specialised materials and enhanced testing increases manufacturing costs, potentially affecting component pricing and profit margins.
- However, the growing ethanol-blended fuel market drives increased volume demand and opportunities for component manufacturers that meet ethanol-compatibility standards.
- Continuous product improvement is essential to maintain competitiveness and supply contracts in an evolving regulatory environment.
5. Innovation Opportunities
- Ethanol fuel adoption drives innovation in advanced fuel-delivery systems, fuel filters, and sealing technologies tailored for ethanol blends.
- Component makers may explore flex-fuel-compatible parts that can handle a wide range of ethanol concentrations, opening new product lines for domestic and export markets.
| Impact Area | Effect | Manufacturer Response |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Need ethanol-resistant polymers, elastomers | Develop new materials and coatings |
| Quality Standards | Higher testing and certification requirements | Implement rigorous ethanol exposure simulations |
| Supply Chain | Shift to ethanol-compatible raw materials | Collaborate proactively with OEMs and suppliers |
| Cost | Increased production and R&D costs | Balance cost with market growth opportunities |
| Innovation | Demand for advanced ethanol-compatible components | Develop flex-fuel compatible parts and solutions |
What are the maintenance tips and things to know about e20 fuel and older motorcycles in India?
There is a dedicated article for the same from our team. Please check out the link below.
What are the long-term costs (fuel, maintenance, and repairs) for ethanol-blended versus regular petrol motorcycles in India?
- E10/E20-compatible motorcycles (post-2023): For motorcycles designed for E10 or E20, there’s minimal extra cost. You might notice a slight drop in mileage (about 2–5%), but this is usually offset by better engine tuning and lower emissions.
- Pre-2023 E10-compatible motorcycles using E20: If you use E20 in a bike only meant for E10, you could see 20–30% higher long-term costs. This is due to accelerated wear and tear, more frequent maintenance, possible component failures, and the risk of losing your warranty.
- Mileage loss is the main factor: In 2025, about 80% of owners reported lower mileage with E20. On average, this meant spending an extra ₹360–1,200 per year just on fuel, due to inefficiency.
- Warranty worries: Using a fuel your bike isn’t built for usually voids the warranty. That means all repairs are your responsibility.
- No price advantage at the pump: As of 2025, E20 costs the same as regular petrol—even though ethanol is cheaper to produce.
Always check if your motorcycle can use E20 before filling up with higher ethanol blends. If your bike is from before 2023, use E10 whenever possible. If you use E20 in a bike not made for it, you might spend an extra ₹13,000–36,000 over five years on maintenance and repairs.
How readily available are E0, E10, E20, or higher blends at fuel stations across India?
By 2025, the availability of ethanol-blended petrol in India depends on the blend. E10 is now the standard fuel everywhere, while E20 is becoming more common.
- E0 (Pure Petrol) Phaseout: Government’s July 2025 amendment to petrol standards quietly eliminated E0 from standard fuel specifications, making it effectively unavailable except for premium 100-octane grades.
- E10 is the Baseline: E10 is now the standard default petrol blend at virtually all retail stations across India. No vehicle owner needs to search for E10; it is ubiquitously available.
- E20 Expansion: E20 availability has surged from 600 outlets (mid-2023) to 12,000+ outlets (2025), with the government targeting complete nationwide coverage by the end of 2025 or early 2026. However, rural and remote areas still have limited E20 access.
- E85 Niche Market: E85 “ETHANOL 100” fuel remains highly limited, available only at select 183 IndianOil stations across 5 states, targeting flex-fuel vehicle owners.
- No Intermediate Blends: Oil companies have adopted an “all or nothing” approach: most petrol pumps offer either E10 or E20; blends like E5 and E15 are not intermediate options in retail.
To sum up, E10 is available everywhere, E20 is spreading quickly, E0 is being phased out, and E85 is only found in a few cities for flex-fuel vehicles.
| Ethanol Blend | Availablity Across India (2025) | Vehicle Compatibilty |
|---|---|---|
| E10 (10%) | Widely available at most petrol stations | Compatible with most petrol vehicles |
| E20 (20%) | Available at select stations in key states | Requires E20-compatible or flex-fuel vehicles |
| E85+ (High) | Not available at commercial fuel stations | Requires dedicated flex-fuel vehicles |
What are the effects on engine longevity, power output, throttle response, or emissions profile for motorcycles?
Ethanol-blended petrol (E10, E20, and higher) affects motorcycles in different ways, including engine life, power, throttle response, and emissions. The effects depend on how much ethanol is in the fuel and whether the engine is designed for it.
1. Engine Longevity
- Ethanol is a solvent that absorbs water, which can lead to increased corrosion and wear in metal parts, fuel lines, seals, and carburettors if the motorcycle is not designed for ethanol blends above E10.
- Properly designed engines and fuel systems with ethanol-resistant components handle E10 well, with minimal impact on longevity. E20 or higher blends require more robust materials and coatings to prevent deterioration over time.
- Using higher ethanol blends in engines not certified for such fuel can accelerate wear, cause deposits, and increase maintenance needs.
2. Power Output
- Ethanol contains about 30% less energy per unit volume than petrol, which can reduce power output and fuel economy if the engine is not recalibrated for ethanol blends.
- Many modern motorcycles adjust fuel injection and ignition timing to compensate for ethanol’s different combustion characteristics, mitigating power loss with E10 and even E20 blends.
- Untuned or carbureted bikes running higher ethanol blends may experience lower power and decreased mileage.
3. Throttle Response
- Ethanol has a higher octane rating and burns faster than petrol, which can improve throttle response and combustion efficiency in ethanol-compatible engines.
- Riders may notice crisper throttle response and smoother acceleration with ethanol blends, especially when the engine management system adjusts for ethanol’s properties.
- In non-optimised engines, throttle response could feel uneven due to mixture issues or fuel delivery adaptation lag.
4. Emissions Profile
- Ethanol blends generally reduce carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC), and particulate matter (PM) emissions through cleaner combustion.
- However, ethanol combustion can increase aldehydes and acetaldehyde emissions, which require advanced catalytic converters to control effectively.
- Ethanol’s higher oxygen content helps lower soot and particulate matter, improving urban air quality compared to pure petrol.
- Modern motorcycles meeting BS6 norms are typically tested and certified on E10 or E20 fuels, ensuring emission controls are optimised for these blends.
| Aspect | Effect of Ethanol Blend (E10/E20+) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Longevity | Minimal impact with E10; higher blends may increase corrosion without ethanol-compatible parts | Requires ethanol-resistant materials for high blends |
| Power Output | Slight reduction in energy density can reduce power if not tuned | Modern EFI bikes compensate; carbureted less efficient |
| Throttle Response | Potential improvement due to higher octane and combustion speed | Engine tuning crucial |
| Emissions | Reduced CO, HC, particulate emissions; possible increase in aldehydes | Requires advanced emission control systems |
What are the long-term costs (fuel, maintenance, repairs) for ethanol-blended versus regular petrol motorcycles in India?
Here is a detailed breakdown of long-term costs for ethanol-blended versus regular petrol motorcycles in India:
| Cost Component | E20-Compatible Motorcycles (Post-2023) | Pre-2023 Motorcycles Using E20 | Pre-2023 Motorcycles Using Regular Petrol | 2025 Industry Data & Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Price per Liter | Rs 100 (approx.) | Rs 100 (approx.) | Rs 100 (approx.) | No price premium despite cheaper ethanol costs |
| Fuel Efficiency (Mileage) | 48-50 kmpl (2-5% loss) | 45-47 kmpl (3-6% loss) | 50 kmpl (baseline) | E20 contains ~7% less energy than pure petrol |
| Cost per km (Fuel) | Rs 2.00-2.08 | Rs 2.13-2.22 | Rs 2.00 | Lower mileage increases per-km fuel cost |
| Monthly Fuel Cost (500 km) | Rs 500-540 | Rs 530-600 | Rs 500 | Based on fuel prices and efficiency loss |
| Annual Fuel Cost (6,000 km) | Rs 12,000-12,600 | Rs 12,900-13,500 | Rs 12,000 | Additional Rs 900-1,500 annually for non-compliant bikes |
| 5-Year Fuel Cost (30,000 km) | Rs 60,000-63,000 | Rs 64,500-67,500 | Rs 60,000 | +Rs 4,500-7,500 extra fuel cost for pre-2023 bikes |
| Annual Fuel System Inspection | Rs 500-1,000 | Rs 1,000-1,500 | Rs 500-1,000 | E20 requires more frequent checks for corrosion |
| Annual Fuel Filter Replacement | Rs 300-600 | Rs 400-700 | Rs 300-600 | Ethanol moisture absorption requires more frequent replacement |
| Annual Carburetor/Injector Service | Rs 800-1,200 | Rs 1,200-1,800 | Rs 800-1,200 | Ethanol deposits cause more frequent cleaning needs |
| Annual Maintenance Cost | Rs 1,600-2,800 | Rs 2,600-4,000 | Rs 1,600-2,800 | Non-compatible bikes face 50-80% higher maintenance |
| 5-Year Maintenance Cost (Total) | Rs 8,000-14,000 | Rs 13,000-20,000 | Rs 8,000-14,000 | +Rs 5,000-6,000 additional for pre-2023 bikes |
| Fuel Line & Seal Replacement | Rs 1,000-2,000 (5-6 year lifecycle) | Rs 2,000-3,500 (2-3 year lifecycle) | Rs 1,000-2,000 (5-6 year lifecycle) | Ethanol’s solvent properties accelerate wear |
| Injector/Carburetor Failure Repair | Rs 3,000-6,000 (after 5+ years) | Rs 3,000-6,000 (after 2-3 years) | Rs 3,000-6,000 (after 5+ years) | Premature failure in non-compliant vehicles |
| Fuel Pump Replacement | Rs 2,500-5,000 (4-6 year lifecycle) | Rs 2,500-5,000 (2-4 year lifecycle) | Rs 2,500-5,000 (4-6 year lifecycle) | Ethanol moisture increases corrosion risk |
| Engine Gasket/Seal Issues | Rs 1,500-3,000 (typical lifecycle) | Rs 1,500-3,000 (earlier failure) | Rs 1,500-3,000 (typical lifecycle) | Ethanol causes swelling/degradation of rubber |
| 5-Year Repair & Replacement Cost | Rs 7,000-14,000 | Rs 8,500-18,000 | Rs 7,000-14,000 | +Rs 1,500-4,000 extra for pre-2023 bikes |
| Warranty Coverage | Fully covered (E20 compatible) | At risk of denial (incompatible fuel use) | Fully covered | Using wrong fuel blend voids warranties |
| Warranty Replacement Cost if Voided | Rs 0 | Rs 2,000-8,000 (owner responsibility) | Rs 0 | Owners bear full cost if warranty denied |
| 5-Year Warranty Cost Impact | Rs 0 | Rs 2,000-8,000 | Rs 0 | Additional risk for pre-2023 bikes |
| Total 5-Year Cost (30,000 km) | Rs 75,000-91,000 | Rs 90,000-113,500 | Rs 75,000-78,000 | Comprehensive lifetime cost |
| Additional Cost vs. Regular Petrol | Rs 0-13,000 | +Rs 15,000-35,500 | Baseline | E20 in pre-2023 bikes costs 20-46% more |
Summary of Key Cost Drivers
- Fuel Efficiency Loss: E20 in pre-2023 bikes reduces mileage by 3–6%, adding ₹4,500–7,500 over five years.
- Maintenance Frequency: Non-compliant bikes require 50–80% more maintenance due to ethanol corrosion, adding ₹5,000–6,000.
- Accelerated Component Failure: Fuel system parts fail 2–3 years earlier in pre-2023 bikes using E20, adding ₹1,500–4,000.
- Warranty Risk: Using incompatible fuel risks warranty denial, potentially costing ₹2,000–8,000 in repairs.
- No Pump-Price Savings: E20 costs the same as regular petrol at the pump, so all cost burden falls on owners through reduced efficiency and increased maintenance.
Recommendation
- E20-Compatible (Post-2023) Motorcycles: Minimal cost increase; E20 usage is economical and environmentally beneficial.
- Pre-2023 Motorcycles: Stick with E10 fuel to avoid an additional ₹15,000–35,500 in costs over five years. Using E20 in non-compatible engines is economically disadvantageous and risks warranty coverage.
What is the roadmap for ethanol blending in petrol in India from 2015 and beyond?
The roadmap for ethanol blending in petrol in India outlines the government’s phased plan to increase ethanol content in fuel to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, cut emissions, and promote biofuels. Here is the roadmap:
1. Initial Phase (Pre-2015 to 2020)
- Introduction of Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme.
- Targeted blending of 5% ethanol (E5) in petrol across major cities and regions.
- Infrastructure development for ethanol supply and production expansion.
2. Expansion Phase (2020-2022)
- Increase blending target to 10% ethanol (E10) nationwide, covering all petrol retail outlets.
- Regulatory standards and vehicle compatibility guidelines were established to support E10.
- Focus on sourcing ethanol primarily from sugarcane and other biomass.
3. Acceleration Phase (2023-2025)
- Scale-up efforts to promote E20 fuel (20% ethanol blend) adoption.
- Support vehicle manufacturers to produce E20-compatible engines and implement warranty policies.
- Strengthening supply chain infrastructure and ethanol production capacity to meet escalating demand.
4. Advanced Phase (2025 and beyond)
- Target full national availability of E20 petrol by 2026.
- Research and pilot projects for higher ethanol blends such as E85 for flex-fuel vehicles.
- Incentives and subsidies for ethanol production from diversified biomass sources to increase sustainability.
5. Regulatory and Monitoring Measures
- Continuous update of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) fuel quality standards to incorporate ethanol blends.
- Emission testing and real-world impact assessment on vehicles using ethanol blends.
- Periodic review and adjustment of blending targets based on market readiness and infrastructure.
6. Environmental and Economic Goals
- Reduce crude oil import dependency by promoting indigenous ethanol production.
- Cut vehicular emissions by replacing fossil petrol with renewable ethanol blends.
- Boost the agricultural economy by creating additional revenue streams for farmers via ethanol production.
| Year/Period | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| Pre-2010s | Ethanol blending mostly absent or minimal (below 5%). |
| Early 2010s | EBP Programme launched;E5 introduced as initial blend. |
| 2018-2020 | Gradual increase in ethanol blending targets,mainly E5 and start of E10 pilot zones |
| 2022-2023 | E10 adoption became widespread, mandated by government targets across India. |
| 2024-2025 | E20 rollout accelerated with infrastructure and compatible vehicle push. |
| 2026+ | Aim for nationwide E20 availability and exploration of higher blends (E85) for flex-fuel vehicles. |
How can bikers verify their model’s compatibility, understand warranty implications, and ensure legal use for E20 petrol in India?
Here is a practical checklist for bikers in India to verify their motorcycle’s compatibility with E20 petrol, understand warranty implications, and ensure legal and safe use:
1. Check Manufacturer Specifications
Review your motorcycle’s owner manual or official manufacturer website for explicit confirmation of E20 fuel compatibility. Look for statements on ethanol blending tolerance or E20 readiness.
2. Contact Official Service Centres
Speak with authorised dealerships or service centres to confirm if your specific model is certified for E20 use. Ask about any recommended modifications or updates required.
3. Verify Fuel System Materials
Ensure the fuel lines, seals, gaskets, and carburettor/injectors are made of ethanol-resistant materials suitable for E20. This may be confirmed by manufacturer documentation or service centre technical advice.
4.Check Warranty Terms
Confirm with the manufacturer or dealership if using E20 petrol affects your motorcycle’s warranty coverage. Some manufacturers may void warranty claims if non-certified fuel blends are used.
5. Look for Official Government or Industry Certification
Verify whether your bike model is on the list of vehicles approved for E20 use by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) or the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas. This provides legal assurance of compliance.
6. Monitor Engine Performance and Behaviour
When trying E20 for the first time, monitor for any unusual engine noises, reduced throttle response, or performance issues. Report any unusual behaviour to the service centre immediately.
7. Fuel Station Verification
Use E20 petrol only at officially approved fuel stations dispensing E20. Verify station signage and quality assurance to avoid adulterated or improper blends.
8. Regular Maintenance
Increase the frequency of fuel system inspections to check for leaks, corrosion, or clogging when using E20 initially. Clean or replace fuel filters as recommended.
9. Stay Updated on Regulations
Follow government notifications regarding fuel quality, ethanol blending levels, and legislative changes affecting fuel use.
10. Keep Records
Maintain records of all manufacturer communications, service centre advisories, and fuel purchase receipts as evidence of compliance and for any warranty claims.
FAQ related to ethanol petrol blending in India
1. Is the octane rating of ethanol actually higher than 100% petrol?
Yes. Ethanol’s octane rating is actually higher than gasoline’s. In some cases, it might even lead to a slight improvement in engine performance.
2. How Does Ethanol Blending Affect Motorcycle Performance?
While ethanol-blended petrol is generally safe for motorcycles, it can slightly decrease fuel efficiency. Motorcycles not designed for higher ethanol blends may experience a 6-7% drop in efficiency compared to four-wheelers and a 3-4% drop compared to two-wheelers.
3. Is E10 petrol available everywhere in India?
Yes. India achieved the E10 blending target well ahead of schedule in June 2022. This means E10 petrol is widely available across the country. Older motorcycles (generally pre-2001) might require adjustments to run smoothly on E10. It’s best to consult a certified mechanic for guidance.
4. Does E10 petrol significantly reduce mileage?
While E10 has slightly lower energy density than pure gasoline, the decrease in mileage is typically 3-7%. This might not be noticeable for many drivers.
5. What is the difference between E10 & E20 fuel in motorcycles?
The critical difference between E10 and E20 petrol lies in the percentage of ethanol blended with regular petrol. E10 petrol contains 10% ethanol and 90% petrol. It’s the standard ethanol blend currently available across most of India. In motorcycles, E20 fuel contains 20% ethanol and 80% petrol. The Indian government plans to introduce E20 by 2025.
6. Is E10 petrol available in India?
Yes, E10 petrol, blended with 10% ethanol, is available in India. In fact, India achieved the E10 blending target well ahead of schedule, reaching it in June 2022.
This means most of the petrol you pump in your bike or car in India is likely E10. The government aims to introduce even higher ethanol blends in the future. They have plans to make E20 petrol (20% ethanol) available nationwide by 2025.
7. What will the cost of E20-compatible motorcycles be in India?
The cost of E20-compatible two-wheelers is expected to range from Rs 1000 to Rs 2000, over and above the price of ordinary gasoline-powered motorcycles.
8. What are the benefits of Ethanol blending?
Ethanol blending offers several benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, decreasing reliance on imported crude oil, and conserving foreign exchange reserves. It also supports the rural economy by promoting the cultivation of crops like maize and sugarcane.
9. Are all motorcycles compatible with E20 Petrol?
Not all motorcycles are compatible with E20 petrol. Older motorcycles may experience issues with corroded engine components. Manufacturers use ethanol-resistant materials to adapt newer motorcycles for E20 compatibility.
10. Are all motorcycles Compatible with E10 fuel?
It is commonly used in internal combustion engines of most modern automobiles without requiring engine modifications.
Here are some related articles from our team
- Motorcycle fuel – Types, things to know & take care in India
- Electric motorcycles & scooters in India: Examining the pros & cons
- Motorcycle fuel tank – How to maintain properly
- Motorcycle fuel – Types, things to know & take care in India
- Electric scooter vs Petrol scooter – Which is best
Conclusion
Ethanol-blended petrol is reshaping India’s fuel landscape, bringing significant changes to the environment, the economy, and technology. It clearly helps lower emissions and supports rural growth, but it also creates new challenges for vehicle compatibility and maintenance.
To make the most of these benefits, it’s essential for motorcycle owners and industry professionals to stay up to date with fuel compatibility, follow manufacturer advice, and adapt to evolving standards as India moves toward higher ethanol blends.
If you have questions or want tips for riding in the monsoon, email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com. We’re happy to help. You can also follow Bikeleague India on social media.