
Long story short: Let’s determine which bike chassis type fits your riding style and if your favourite motorcycle has it.
Key Takeaways
- The motorcycle’s chassis, or frame, connects all its parts. It functions like a skeleton in the human body.
- Backbone frames are commonly found in low-cost motorcycles with smaller engines; however, manufacturers are shifting away from this design due to its limitations.
- A Single cradle frame is also known as a single downtube or diamond tube frame.
- Double cradle frame is also known as Twin down tube spine frame.
- The perimeter frame, also known as a twin-spar frame, is a modern chassis commonly found on many high-performance motorcycles.
- The trellis frame is similar to the perimeter frame. Still, it features a lattice-like design with tubes to provide strength, rigidity, and a lightweight structure.
What is a bike chassis/frame? Why is it so crucial?
The motorcycle’s frame connects all its parts. It functions like a skeleton in the human body. A frame directly affects handling and ride quality. Motorcycles come in various body styles and have distinct frame types. For details about motorcycle types by body, see this article. Key frame components include the frame itself, front fork, and suspension.
Different types of bike chassis/frames
1. Backbone frame
A backbone frame connects the engine to the chassis, linking the rear suspension’s steering head to the pivot point. The engine helps support the bike. This frame, shaped like a spine, is simple and affordable but offers less strength and rigidity than other types. Manufacturers are shifting away from this design.
Advantages of backbone frame
- Low manufacturing cost, making bikes more affordable.
- Simple construction with fewer materials, reducing overall weight.
- Suitable for commuter and entry-level motorcycles due to its basic structure.
- Offers decent handling and stability for low-powered motorcycles.
- Even weight distribution due to the central spine structure.
Disadvantages of backbone frame
- Lacks rigidity and structural strength, making it unsuitable for powerful engines.
- Poor torsional rigidity, which affects handling at higher speeds or with aggressive riding.
- Minimal protection in case of side impacts or crashes.
- Not ideal for heavy modifications or demanding riding conditions.
Examples
2. Single cradle frame (Single downtube / Diamond tube)
Single-cradle frames are seen on budget motorcycles and resemble bicycle frames. Welded steel tubes hold the engine, which sometimes also supports the frame. Lightweight and inexpensive, this design can feel unstable during hard braking or sharp turns.
Advantages of single cradle frame
- Cost-effective and easy to manufacture, ideal for entry-level motorcycles.
- Lightweight structure improves fuel efficiency and manoeuvrability in urban traffic.
- Simple design allows for ease of maintenance and repairs.
- Adequate balance and stability for low-power bikes designed for daily commuting.
Disadvantages of single cradle frame
- Limited strength and torsional rigidity, unsuitable for high-performance and heavy motorcycles.
- Can be prone to flex under heavy loads, aggressive riding, or hard braking.
- Offers less crash protection compared to more robust frame types.
- Not recommended for off-road or sporty handling requirements.
Examples
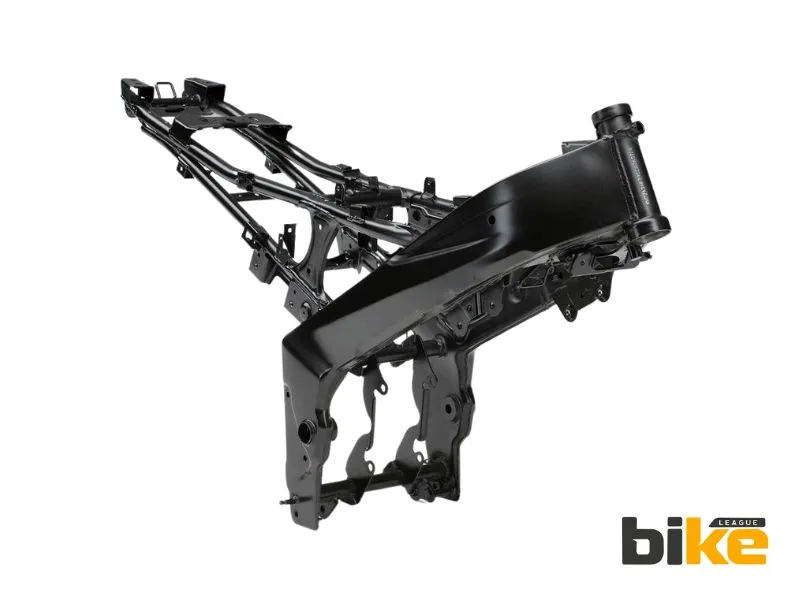
3. Double cradle frame (Twin down tube spine frame)
A double-cradle frame uses two tubes under the engine, rather than one. This makes the frame affordable, stronger, and more rigid. It handles heavy braking and lean angles well, but newer frame designs are preferred for high-performance bikes.
Advantages of double cradle frame
- Provides better structural strength and rigidity compared to single cradle frames.
- Cost-effective solution for supporting larger engines and heavier motorcycles.
- Offers improved stability and handling by reducing frame flex under stress.
- Easier to manufacture and maintain compared to high-performance frame types like perimeter or trellis.
Disadvantages of double cradle frame
- Heavier than single cradle frames due to additional tubes, which can slightly reduce fuel efficiency.
- Generally considered an older design, less suited to high-performance sportbikes.
- A Bulkier frame design can increase weight and limit agility compared to perimeter frames.
Examples
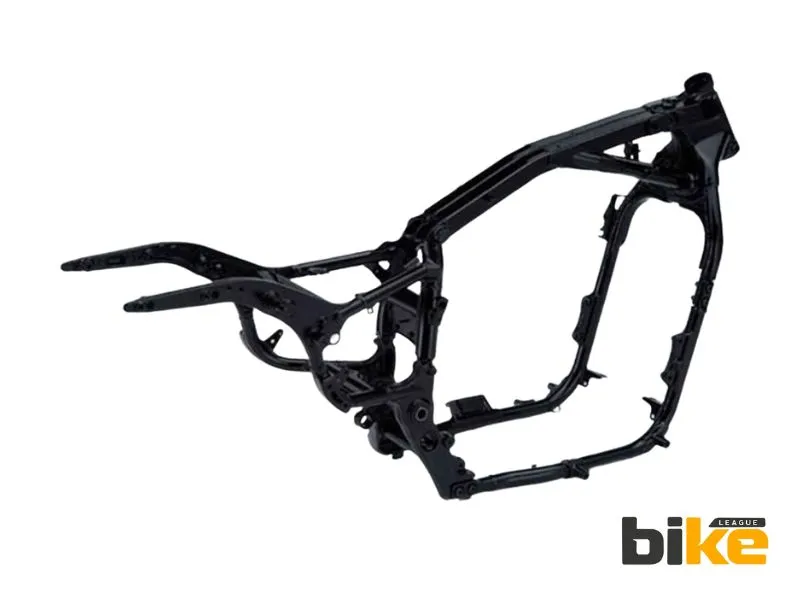
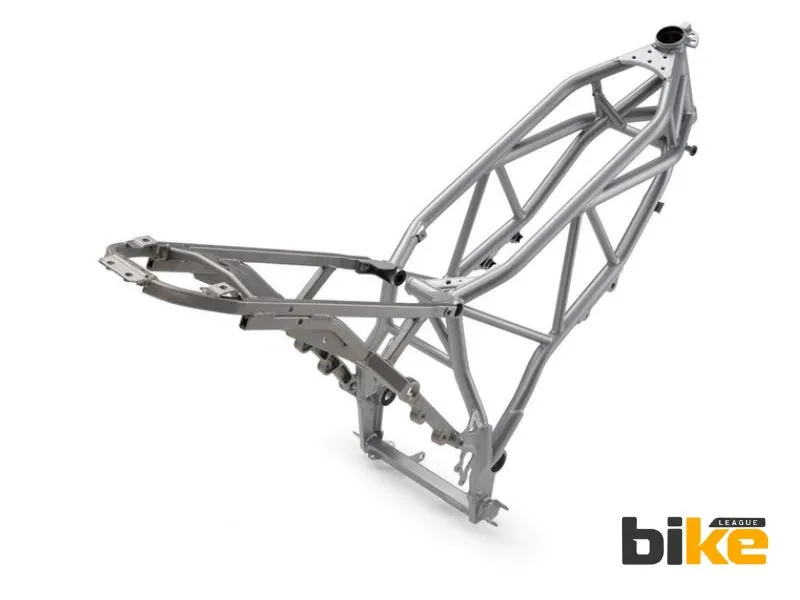
4. Perimeter frame (Twin Spar Frame)
The perimeter frame, also known as a twin-spar frame, is a common feature on high-performance motorcycles. Its beams connect the steering head to the swingarm efficiently, making it stiff and light while surrounding the engine. Most are aluminium. This design offers excellent stability and rigidity.
Advantages of Perimeter frame
- Excellent structural rigidity and torsional stiffness, enhancing stability at high speeds and during aggressive cornering.
- Lightweight construction, often made from aluminium, improves power-to-weight ratio and handling agility.
- Connects the steering head directly to the swingarm pivot in the shortest distance, optimising handling precision and sharpness.
- Enhances the bike’s ability to maintain lines through corners, offering superior riding dynamics compared to cradle or backbone frames.
- Used extensively by MotoGP teams and top-tier performance motorcycles globally and in India.
Disadvantages of Perimeter frame
- Relatively costly to manufacture due to aluminium construction and precision required in welding and machining.
- Can be complex to repair if damaged compared to simpler frames.
- Less common in mass-market commuter bikes in India because of cost and manufacturing complexity.
Examples
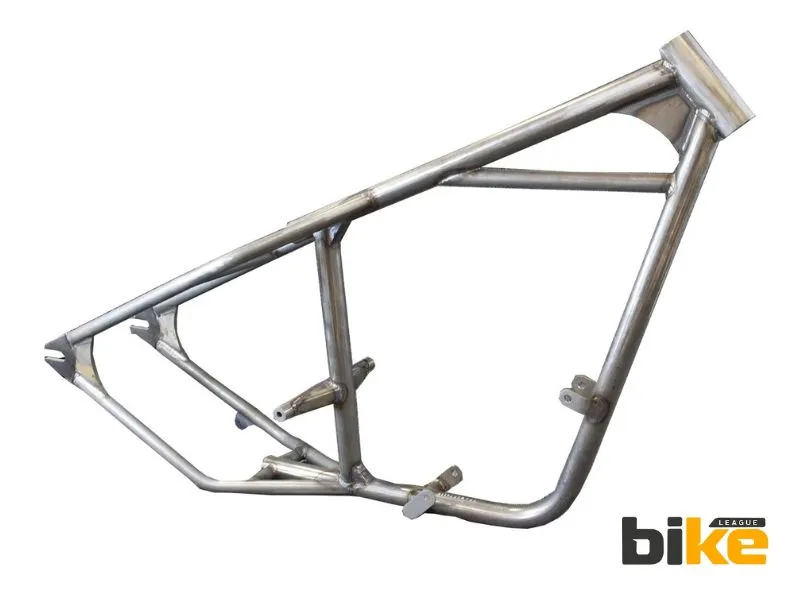
5. Trellis frame
The trellis frame is similar to the perimeter frame. Still, it features a lattice-like design with tubes to provide strength, rigidity, and a lightweight structure. Trellis frames are lighter and stiffer than perimeter frames, easier to build, and offer extra strength.
Advantages of Trellis frame
- Lightweight construction improves agility and overall speed.
- High strength and rigidity ensure excellent handling and stability through corners.
- Greater load distribution across multiple tubes enhances durability and structural integrity.
- Good accessibility to the engine and components for easier maintenance.
- Vibrations are dampened by the frame design, improving rider comfort.
- Relatively simpler manufacturing process using standard tubes and welding.
Disadvantages of Trellis frame
- Labour-intensive welding process requiring skilled craft, raising manufacturing and repair costs.
- Exposed frame may not appeal aesthetically to riders preferring sleeker designs.
- More joints and tubes require frequent inspection for cracks or fatigue.
- Less protection for the engine from dust and debris due to the open structure.
- Frame design can restrict space for accessories or customisation.
Examples
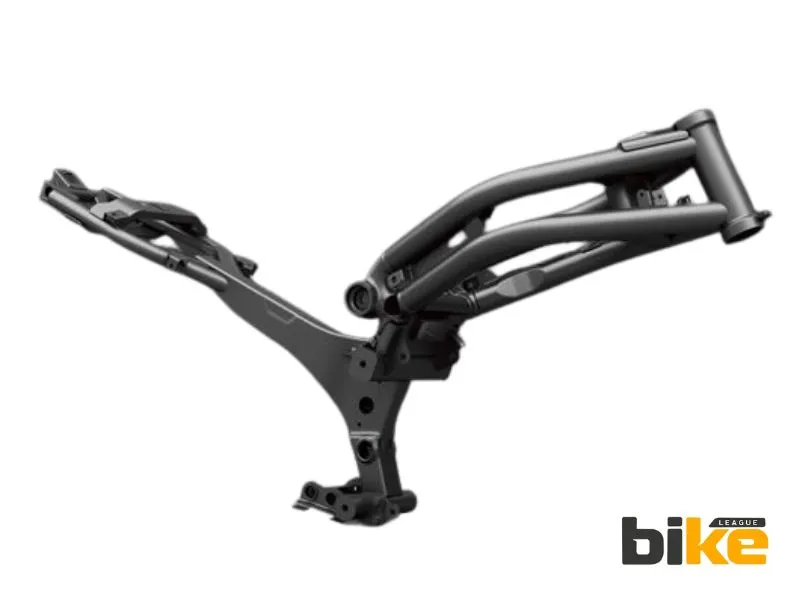
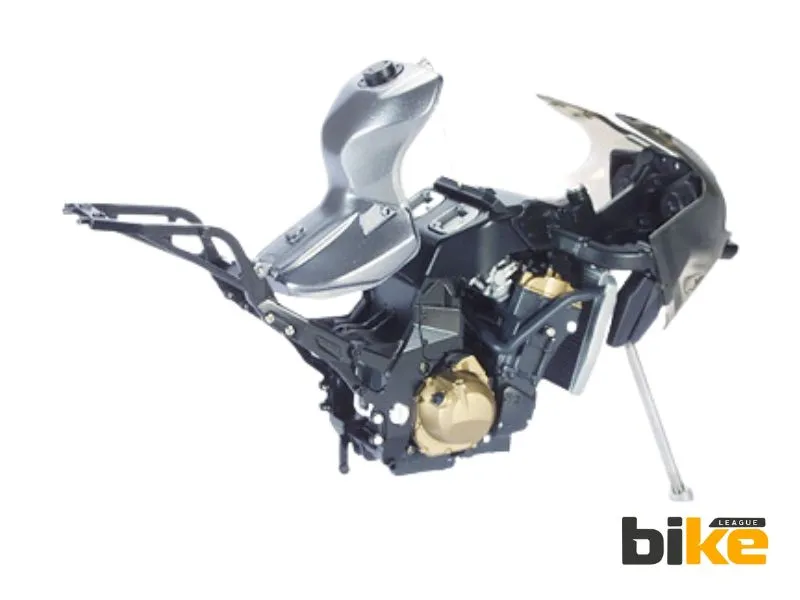
6. Monocoque frame
Monocoque frames are made in advanced factories and tend to be expensive. The whole frame is a single, very rigid piece. These frames are designed for powerful motorcycles that require maximum strength and minimal weight. They often use materials like carbon fibre and magnesium, which add to the cost.
Advantages of Monocoque frame
- Lightweight design improves acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency due to reduced mass.
- Superior rigidity distributes stresses evenly, enhancing stability and rider control, especially at high speeds.
- Offers better crash safety as the integrated frame can absorb and dissipate impact forces more effectively.
- Increased interior space and packaging efficiency due to the absence of a separate frame.
- Improved ride quality from reduced flex and vibrations.
Disadvantages of Monocoque frame
- Complex and costly to manufacture and repair compared to traditional frame types.
- Less suited for heavy off-road use or rugged conditions as the unified structure is less tolerant to extreme stresses.
- Limited flexibility for modifications or customisations due to integrated design.
- Lower towing capacity compared to body-on-frame designs in the automotive context, although less relevant for motorcycles.
Examples
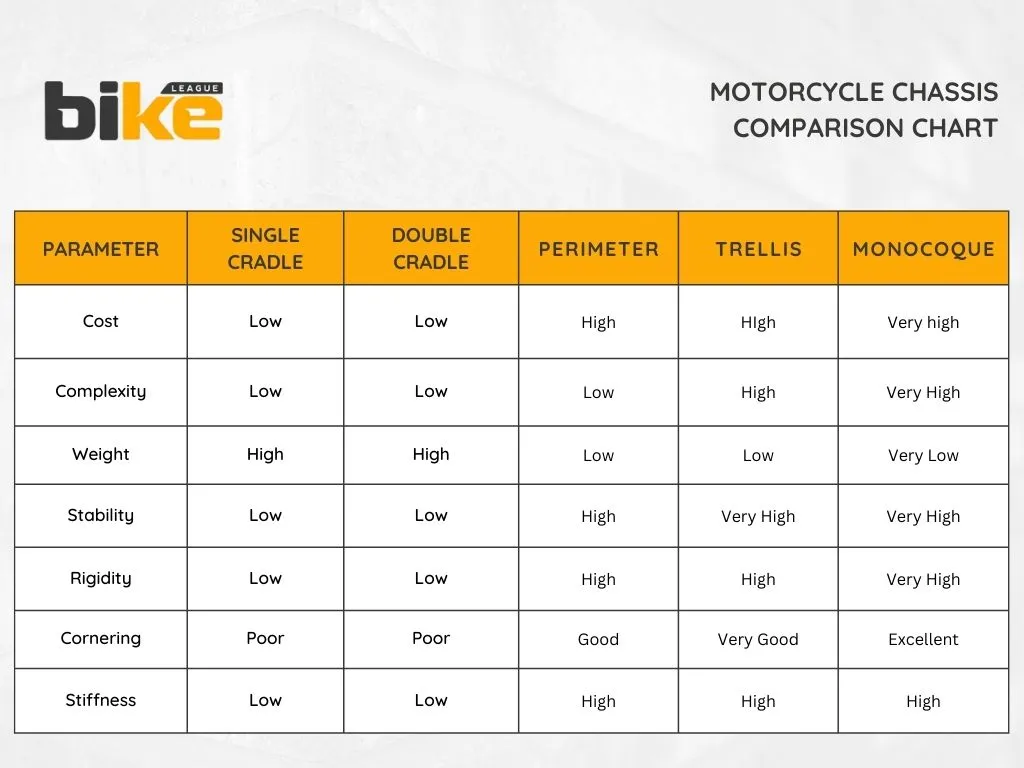
Comparison of of different types of motorcycle chassis
| Chassis Type | Features | Pros | Cons | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone Frame | Single large tube running from steering head to rear | Simple, very cost-effective, lightweight | Low torsional rigidity, less structural strength | Kawasaki Ninja 300 |
| Single Cradle Frame | Single downtube loop cradling the engine | Cost-effective, light, easy to maintain | Moderate rigidity, not ideal for high-performance | TVS Star City Plus, Honda Shine 100 |
| Double Cradle Frame | Two tubes cradling the engine for better strength | Stronger and more rigid than single cradle | Heavier than single cradle, older design | Yezdi Roadster, Royal Enfield Bear 650 |
| Perimeter Frame | Twin spars from steering head to swingarm | Excellent rigidity, lightweight, great handling | Complex and expensive manufacturing | Bajaj Pulsar 200NS, Bajaj Dominar 400 |
| Trellis Frame | Welded tubes forming a triangular lattice | High strength-to-weight, agile handling | Labour-intensive build, needs regular inspection | KTM Duke 200, TVS Apache RTR 310, BMW G 310 R |
| Monocoque Frame | Integrated chassis and body as one shell | Very rigid, lightweight, good crash protection | Very complex and costly to manufacture & repair | Ducati Panigale V2, BMW R18 Transcontinental |
What is the role of wheelbase in a bike chassis?
The wheelbase is the distance between the centres of a motorcycle’s front and rear wheels. This measurement is crucial because it affects how the bike handles and its overall stability. The wheelbase can give you a good idea of how a motorcycle will perform in different situations.
1. Short wheelbase
Bikes with a short wheelbase are agile and easy to handle. They turn quickly and are straightforward to manoeuvre in tight spots, making them great for city riding and race tracks. Their nimbleness also helps with stunts like wheelies and stoppies.
2. Long wheelbase
On the other hand, a long wheelbase gives a bike more stability, especially at high speeds on highways. This makes long-wheelbase motorcycles more comfortable for long rides, since they are less likely to wobble. However, they are usually less agile in corners than bikes with a shorter wheelbase.
| Aspect | Shorter Wheelbase | Longer Wheelbase |
|---|---|---|
| Handling | More nimble and agile, quicker turns | More stable at high speeds, less twitchy |
| Stability | Less stable at high speeds, prone to wobble | Enhanced straight-line stability |
| Cornering | Easier to lean and maneuver in tight corners | Requires more effort to initiate turns |
| Ride Comfort | Can be less comfortable on rough surfaces due to shorter frame | Smoother ride, better shock absorption |
| Suitability | Ideal for sportbikes, urban commuting | Preferred for cruisers, touring motorcycles |
| Rider Confidence | More responsive but can be challenging for beginners | More confidence-inspiring due to stability |
| Weight Distribution | Concentrated near center, aiding agility | Spread out for better load management |
| Examples in India | Yamaha R15, KTM Duke 200 | Royal Enfield Classic 350, Bajaj Dominar 400 |
How do the chassis types impact the overall safety of the motorcycle?
The type of motorcycle chassis has a considerable impact on overall safety, primarily through its effects on structural rigidity, crash protection, stability, and handling dynamics.
1. Structural Integrity and Crash Safety
- Chassis designs with high stiffness (like perimeter, double cradle, and trellis frames) better maintain structural integrity during collisions, helping distribute and absorb impact forces across the frame.
- A strong, well-designed frame minimises the risk of catastrophic failure, protects critical components such as the engine, and can prevent secondary accidents after the initial impact.
- Backbone frames and lightweight single tube designs, while cost-effective, may offer less protection in severe impacts because of lower rigidity and fewer load paths.
- Fatigue resistance and proper distribution of stresses are critical for long-term safety; poorly designed frames can lead to cracks or buckling under repeated loads.
- Accessories like crash bars and frame sliders, fitted to robust chassis designs, further improve crash performance by providing sacrificial protection, absorbing energy, and reducing damage to vital areas.
2. Stability and Handling Impacts
- Frame geometry, weight distribution, and torsional stiffness directly influence handling and stability, which are foundational for accident prevention.
- High rigidity frames (perimeter, trellis) reduce frame flex during braking and cornering, preserving tyre contact and control, especially at higher speeds.
- Poor chassis balance or excessive frame flex makes a motorcycle prone to instability, unpredictable handling, and dangerous oscillations (such as tank-slappers), raising accident risk.
- The choice of chassis must align with riding style and use case; an unsuitable frame geometry can be a safety risk, especially on challenging terrain or in emergency manoeuvres.
3. Material Selection and Build Quality
- Advanced materials like high-tensile steel and aluminium alloys used in modern frame designs reduce weight without compromising structural strength, improving agility and crashworthiness.
- Proper welds, joint integrity, and manufacturing precision are critical—flaws in the frame’s construction can be a hidden safety hazard, potentially causing frame failure during an accident.
In summary, selecting the right chassis type and ensuring its structural integrity directly enhances both crash safety and accident prevention, making frame design a key contributor to a motorcycle’s overall safety profile.
FAQ related to different types of bike chassis/frames
1. What role does the wheelbase play in a motorcycle chassis?
The wheelbase, the distance between the front and rear axles, is critical to a motorcycle’s stability and manoeuvrability. A longer wheelbase generally provides better stability at high speeds, while a shorter wheelbase enhances manoeuvrability.
2. What is the significance of frame stiffness?
Frame stiffness is crucial for handling and stability. A stiffer frame can improve the motorcycle’s responsiveness and control, especially during cornering and high-speed riding. However, excessive stiffness can also lead to a harsh ride, so a balance is necessary.
3. Which motorcycle frame material is best?
For budget-oriented motorcycles, the steel tube is the main component and is welded according to requirements. Steel is very cost-effective and robust, but it is not lightweight. However, the chassis should be both light and stiff when we enter the performance motorcycle market. Therefore, aluminium and its alloys are utilised to achieve these advantages. Carbon fibre, magnesium, and titanium materials are used for ultra-performance racing bikes and street bikes.
4. Which motorcycle frame is the best?
The monocoque frame is undoubtedly the best, but it is also the most costly. The trellis and perimeter frame are in the second spot.
5. Which bike frame is the lightest?
Carbon fibre, magnesium, and titanium material frames have the least weight.
6. What type of bike frame is best suited for aggressive riding?
The perimeter frame and trellis frame are the best. KTM and Ducati use trellis frames for most of their models.
7. Which bike frame do budget-friendly bikes use?
Budget-friendly bikes typically use single-cradle frames nowadays. Earlier backbone frames were present in entry-level models.
8. Is there a size for motorcycle chassis?
No. There are no various size types, so we can select them according to size or weight. Motorcycle companies design bikes for a range of riders, taking into account both height and weight.
9. Can we replace the bike chassis?
Motorcycle chassis can be repaired or replaced, but this is typically done only at official service centres. A replacement scenario occurs when a major accident or damage to the chassis occurs. Otherwise, technicians will try to repair the damage. If significant damage occurs to the bike chassis, investing in a new bike will be a better option.
10. How do I find the bike chassis number?
The chassis number is present near the bike’s handle or motor. If you find it challenging to locate your motorcycle, you can seek the help of a mechanic. The owner’s manual and registration certificate mention the bike’s chassis number.
11. Why do performance motorcycles use perimeter frames?
Perimeter frames offer high torsional rigidity and lightweight construction, providing superior handling and stability at high speeds.
12. What is a trellis frame, and why is it popular in performance bikes?
A trellis frame utilises welded tubes arranged in a triangular pattern, providing an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and precise handling.
13. How to get a motorcycle chassis number online?
Follow the steps below to find the chassis number.
- Visit the official website of Vahan NR e-Services. Select “Know Your Vehicle Details.”
- Log in with your registered mobile number. Register with your mobile number and email ID if you are using this portal for the first time.
- Enter details of your vehicle and the captcha. Select “Search Vehicle.”
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Braking in motorcycle – All expert tips for bikers
- Second hand motorcycle: Things to know when buying It
- Bike number plates in India – Detailed Guide & Video
- Swingarm types in motorcycles : Exploring different ones
- Motorcycle Fancy number – How to get your favorite one
Conclusion
We’ve covered the different types of bike chassis and frames, their pros and cons, and answered some common questions. If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com or leave a comment below. We’re always happy to help. You can also connect with us on Bikeleague India’s social media platforms.








This is the perfect guide for picking out your bikes skeletal structure! Who knew a tube here or a cradle there could make such a difference? Seriously though, its hilarious how some frames are just affordable while others are complex and costly. I love the part about wheelbases – apparently, if you want to look cool making U-turns, get a short one; if you prefer stability (and maybe avoiding awkward conversations with your bike), go long. And the grand finale: monocoque frames are undoubtedly the best but also the most costly. Makes you wonder if youre just paying for a really fancy rectangle! Great read for anyone trying to decide if their next ride should be a simple backbone or a complex monocoque.